Institute: University of Florida, Gainesville, FL, USA
Clinical history: 27 year-old male with the history of heterotaxy syndrome, extreme form of Tetralogy of Fallot with pulmonary atresia, and right aortic arch. At 14 years of age, the patient underwent placement of a central shunt which subsequently clotted, followed by right modified BT shunt one year later.
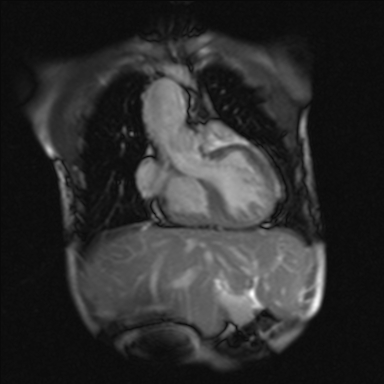
Figure 1: Midline liver
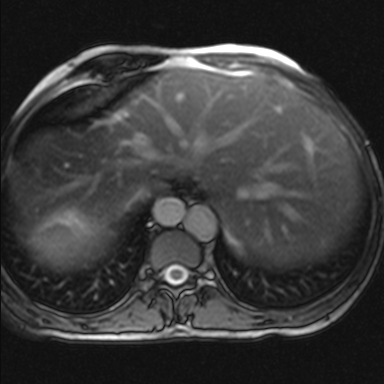
Figure 2: Interrupted IVC with aorta on the right and azygos continuation on the left
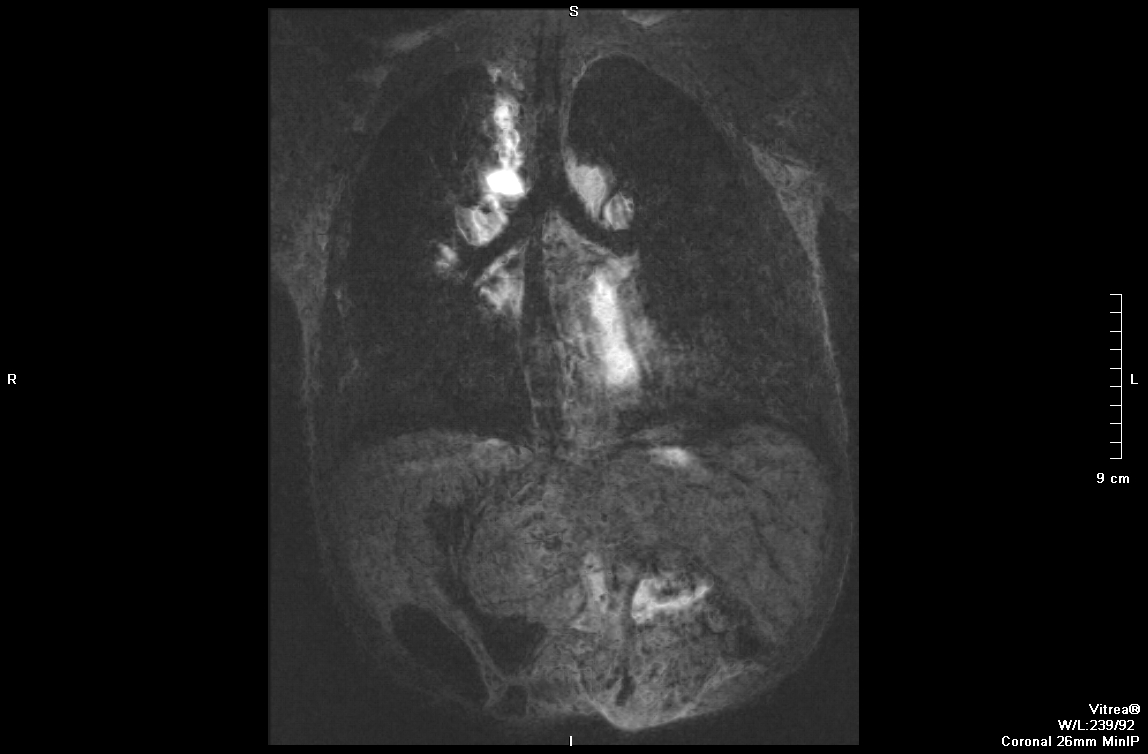
Figure 3: Bilateral left bronchi
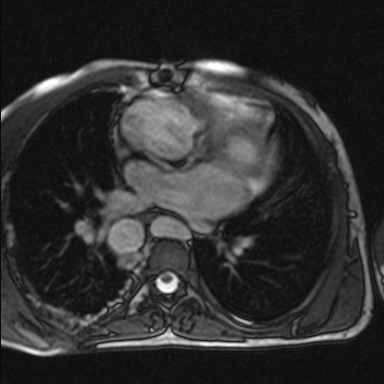
Figure 4: Left-sided morphologic left atria
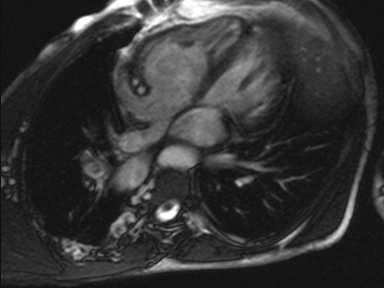
Figure 5: Right-sided morphologic left atria
There are findings of tetralogy of Fallot with pulmonary atresia, right ventricular hypertrophy, membranous VSD, and overriding aorta (Movie).
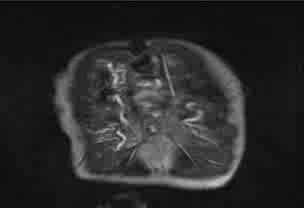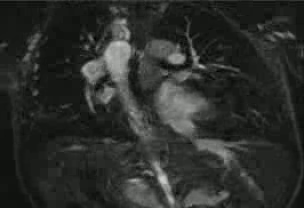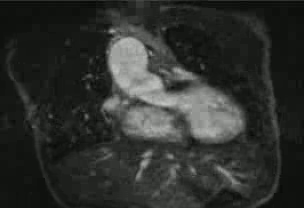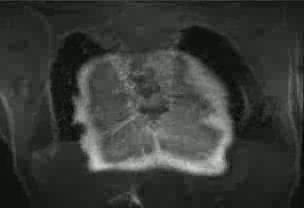
Movie: Pulmonary valve atresia with small contiguous right and left main pulmonary arteries, right ventricular hypertrophy, membranous VSD, and overriding aorta
The azygous vein drains into a left SVC. The left SVC and suprahepatic IVC drain into the left-sided atrium.
The right-sided ventricle is the morphologic right ventricle and is hypoplastic with pulmonary atresia. The left-sided ventricle is the morphologic left ventricle, which supplies a right-sided three-vessel aortic arch. There is a large perimembranous ventricular septal defect.
There are small contiguous pulmonary arteries. There are multiple major aortopulmonary collateral arteries, which supply the lungs and the pulmonary arteries. A few small collateral arteries arise from the undersurface of the distal arch and supply flow to bilateral pulmonary arteries. An additional collateral artery arises from the posterior aspect of the mid descending thoracic aorta and supply the right lung. More inferiorly, a collateral artery arises from the medial aspect of the descending thoracic aorta and supplies the left lung. The previously placed central shunt and modified right BT shunt are no longer patent.
The coronary arteries are also ectactic, which has previously been described with congenital heart disease.
Quantitative data is as follows:
ASCENDING AORTA FLOW QUANTIFICATION:
Forward volume (ml): 145
Reverse volume (ml): 20
Regurgitant fraction: 14 %
Net Forward Volume (ml): 125
RIGHT PULMONARY ARTERY FLOW QUANTIFICATION:
Forward volume (ml): 17
Reverse volume (ml): 0
Regurgitant fraction: 0
Net Forward Volume (ml): 17
LEFT PULMONARY ARTERY FLOW QUANTIFICATION:
Forward volume (ml): 24
Reverse volume (ml): 0
Regurgitant fraction: 0
Net Forward Volume (ml): 24
LEFT VENTRICULAR ANALYSIS:
Ejection fraction of 57%
Average mass is 92 g
End diastolic vol is 222 ml
End systolic vol is 95 ml
Stroke volume is 127 ml
Cardiac output is 7.7 L/min
RIGHT VENTRICULAR ANALYSIS:
Ejection fraction of 57%
End diastolic volume is 115 ml
End systolic volume is 49 ml
Stroke volume is 66 ml
Cardiac output is 4.0 L/min
BSA: 1.65m2
Conclusion:
Note: The sum of right ventricle stroke volume and left ventricle stroke volume (66 ml + 127 m l= 193 ml) should theoretically be equal to the sum of the forward flow in the ascending aorta (145 ml) if no AV-valve regurgitation is present. With these numbers the patient has a total theoretical AV-valve regurgitation (we cannot differentiate between MR and TR with only these numbers) of 28 %:
{100 x [(RVSV+LVSV)- AoA forward flow] } / [(RVSV+LVSV)- AoA backward flow] = {100 x [193ml-145ml] } / [193ml-20ml] = 28%
There was only trivial TR and no MR on echo. The cine CMR images showed only TR and no MR. Utilizing variables from 2 different type of quantification modalities to derive a 3rd variable is sometimes subject to an accumualtion of minor errors resulting in a final more wayward answer especially in complex cases such as this one.
Tetralogy of Fallot with pulmonary atresia can range from only atresia of the valve to complete absence of the pulmonary arteries. In patients with prominent collateral vasculature, the surgical repair is usually staged. Antegrade flow from the right ventricle to the pulmonary arteries may initially be restored with a modified shunt or with unifocalization of the pulmonary arteries. This is performed by anatomizing the aorticopulmonary collateral vessels to the reconstructed pulmonary artery after severing their connections to the aorta. These patients require follow-up as there is a tendency for the anatomized vessels to become stenotic.
Perspective:
This patient was difficult to evaluate with echocardiogram given prior median sternotomy and scar formation. In this case Qp / Qs cannot be calculated using the flow measurements in the RPA, LPA and ascending aorta because of the presence of other collaterals. The average oxygen saturation for this patient was 77% on room air. Echocardiogram would have also provided very limited information regarding aortopulmonary collaterals. In addition, cardiac catheterization was avoided due to the patient’s polycythemia and increased thrombotic risk. Preoperative planning, with mapping of the major aorticopulmonary collaterals, was able to be performed with MR imaging alone.
Cardiac MR serves as a useful, necessary, and optimal imaging tool in patients with congenital heart disease. MR can provide both functional and morphological information without the expense of radiation. Most of these patients will need not only an initial evaluation to determine anatomy, but numerous subsequent evaluations to re-evaluate and monitor function following intervention. In our case, MR was also useful in determining differential blood flow to the lungs and can evaluate the hemodynamic significance of any vascular stenosis.
References:
COTW handling editor: Sohrab Fratz, MD, PhD
Have your say: What do you think? Latest posts on this topic from the forum